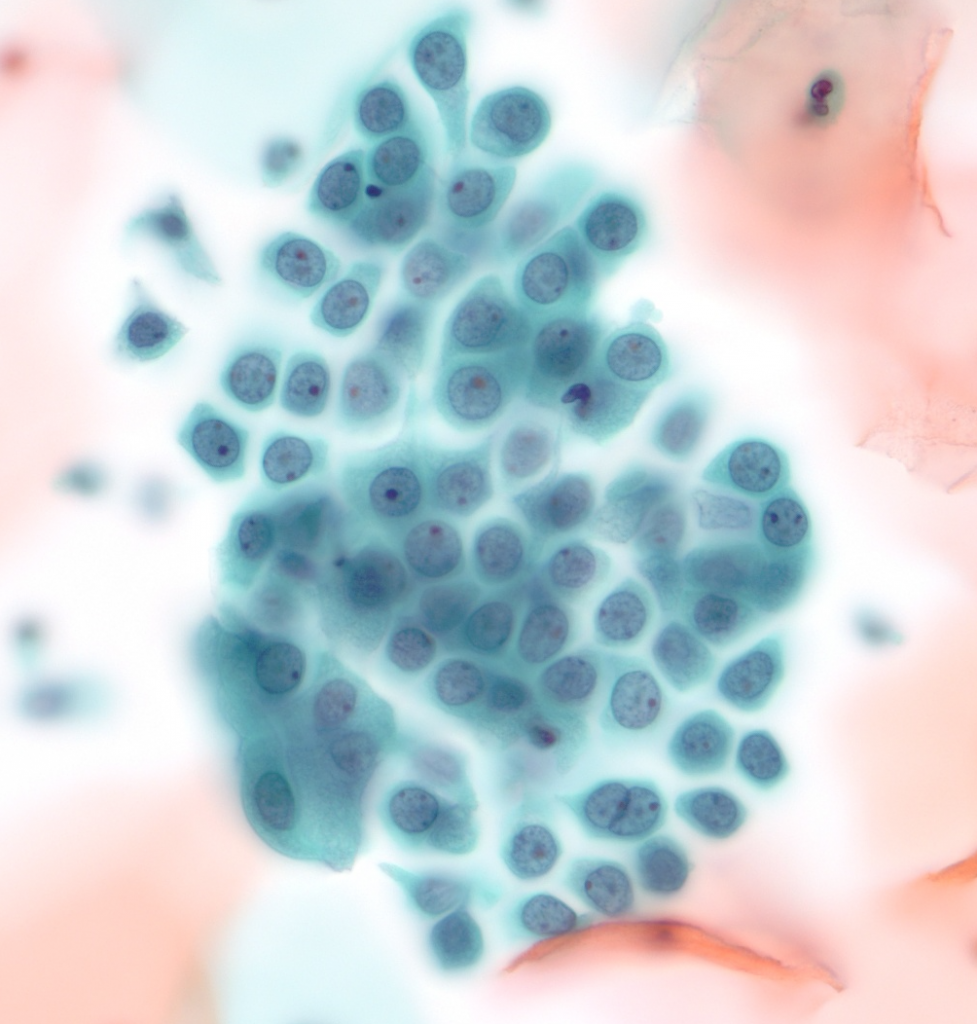
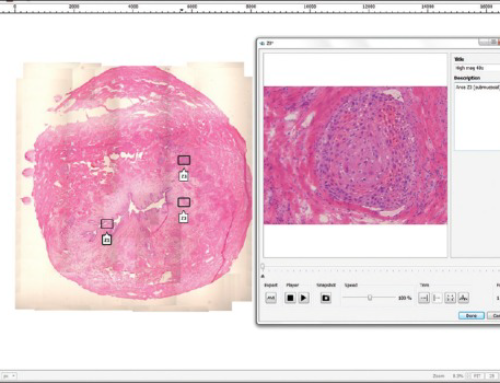
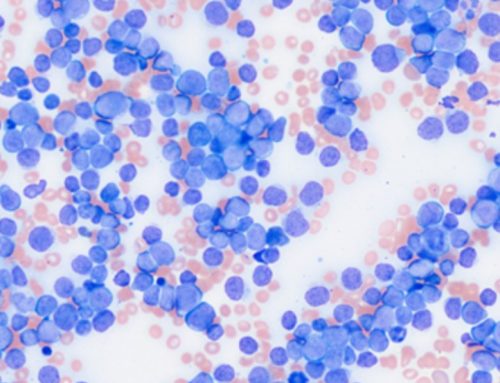
Application of microscope-based scanning software (Panoptiq™) for the interpretation of cervicovaginal cytology specimens
Ruben Groen, Kuniko Abe, Han-Seung Yoon, Zaibo Li, Rulong Shen, Akira Yoshikawa, Takao Nitanda, Yukiko Shimizu, Isao Otsuka, Junya Fukuoka
Cancer Cytopathology Vol. 125, Issue 12, December 2017; Pages 918-925
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the viability of Panoptiq™ for the digital interpretation of cervicovaginal cytology specimens compared to that of conventional microscopy for diagnostic reads.
For this evaluation 100 LBC slides were selected, dotted, reviewed and scanned at 20X magnification with Z-stacks. The washout time between digital and conventional glass slide review was 3 weeks. Of the reviewers, 3/5 achieved a concordance rate ranging from 81.2% to 89.6%.
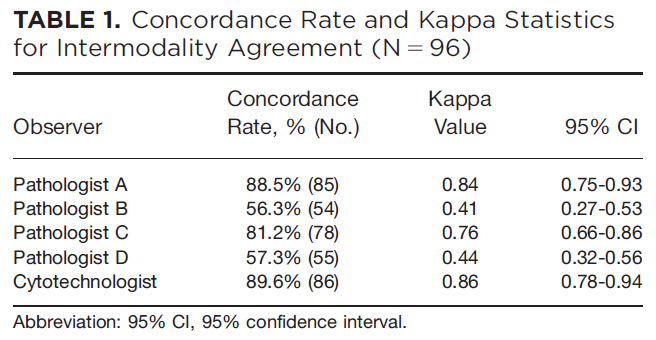
The cases were reviewed by 4 pathologists with >30 years experience and one board certified cytotechnologist.
Initial comments from the participants included:
- “Image quality of Panoptiq™ [was] equivalent to [that] of glass slides”
- “Time to formulate a [diagnosis] was shorter with Panoptiq™”.
- “Scanning took more time for cases with single or isolated cells vs. large atypical cell groups” (pre-scanning observation delay)
- There were also some HSV inclusions picked up with Panoptiq™ software which had been missed on conventional microscopy review.
- “Scan time was <5 minutes and the file size was <500MB”.
- All pathologists expressed their willingness to use it for education/teaching (CME)
The study was limited by a small sample size and included only cervico-vaginal cytology. Training of observers was not enforced. It was also observed that image acquisition was dependent on the skill of the cytotechnologist to scan the region of interest and that prior exposure to viewing of digitized images aided in accurate diagnosis.
Panoptiq™ can be used on any camera-mounted brightfield microscope and works to digitally stitch together multiple fields of view into a single image file in real time. It can also digitize at multiple magnifications and focus planes (Z-stacks). It enhances cytology work flow by its ability to simultaneously scan and screen images.