Evaluation of panoramic digital images using Panoptiq™ for frozen section diagnosis
Dinesh Pradhan, Sara E Monaco, Anil V Parwani, Ishtiaque Ahmed, Jon Duboy, Liron Pantanowitz. J Pathol Inform. 2016 May 4; 7:26
This study evaluated the performance of Panoptiq™ software for frozen section diagnosis in remote consultations. Telepathology and digital imaging of anatomical pathology samples via frozen sections has been increasing through the pathology field for efficiency of diagnosis and improving overall patient care. By conducting consultations in a digital manner, patients are able to have diagnostic reviews by expert pathologists who are not located in the same hospital where their procedures are being conducted.
In this study, a total of 20 genitourinary pathology samples were randomly selected which included benign, atypical and neoplastic cases. Single H&E glass slides were used and included 60 total images/slides reviewed.
A pathology resident manually acquired all Panoptiq™ panoramic digitized images by creating base scans of 4X magnification and selected regions of interest for Z-stack capture at 40X magnification. The Panoptiq™ camera captures Z-stack videos at 15 frames per second and regions of interest were captured at 40X magnification by focusing up and down using the microscope’s fine focus knob. By adding multiplanar Z-stacking, this allowed the ability to overcome focusing problems compared to single Z-plane whole slide imaging. Acquisition of Panoptiq™ images is operator dependent and requires adequate training in digital microscopy.
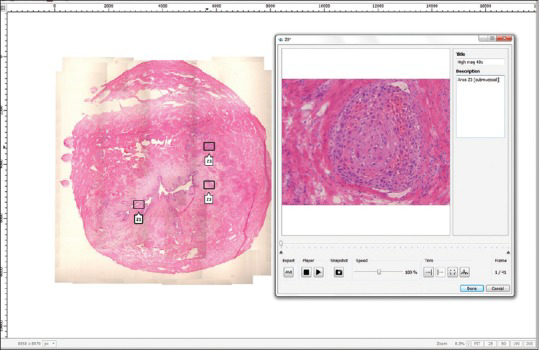
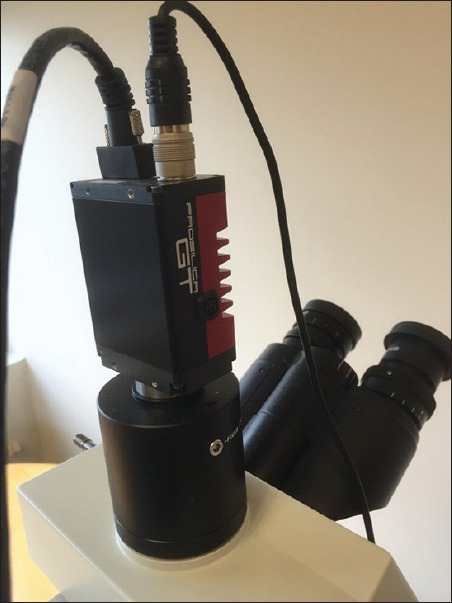
Three board certified pathologists examined l glass slides on a conventional microscope, WSI Aperio system using ImageScope Software and on a conventional microscope with the Panoptiq™ software system. Panoptiq™ system comprised a Prosilica GT camera attached to an Olympus Bx 45 microscope and DELL Precision Tower 810 computer. Panoptiq™ 3 version 3.1.2 software was used for image acquisition. The pathologists were blinded to the original diagnosis and had a washout period of two weeks.

The results showed diagnostic concordance of 98.3% and 100% with Panoptiq™ and Aperio WSI respectively in comparison with glass slides . Panoptiq™ image quality was found to be superior to the Aperio WSI. In addition Panoptiq™ was better able to focus through tissue folds and air bubbles in z-stacked files. The diagnostic confidence recorded was 93% and 85% with Panoptiq™ and WSI respectively.
Image size was also a comparable consideration in this paper. It was found that image sizes of Panoptiq™ scans (25,029 KB; 200-300MB/Z-stack) were approximately 14 times smaller than that of the Aperio WSI (177,000 KB).
Some limitations for completing these consultations was that a histotechnologist may lack the diagnostic expertise to capture the regions of interest and that an on-site pathologist or pathology resident is required for a real-time consultation. At the time of this paper being written, it was also noted that for real-time review, bi-directional dialog is needed between the person acquiring the image and the remote pathologist. This tool is now available in the most recent version of Panoptiq™ software, and allows remote viewers to mark areas of interest directly on the scanned slide as it is being stitched together.